A solar tracker is a pivotal innovation in solar technology as it revolutionizes how we harness solar energy. These dynamic systems adjust the orientation of solar panels or reflective surfaces to follow the sun's trajectory across the sky. This alignment significantly boosts the efficiency of solar panels, potentially increasing energy output by up to 40% compared to ordinary panels.
With advancements in solar trapping technology, solar trackers have found widespread application in residential and commercial solar installations. This article will discuss the various types of solar tracking systems and explore their unique advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Solar Tracking Systems
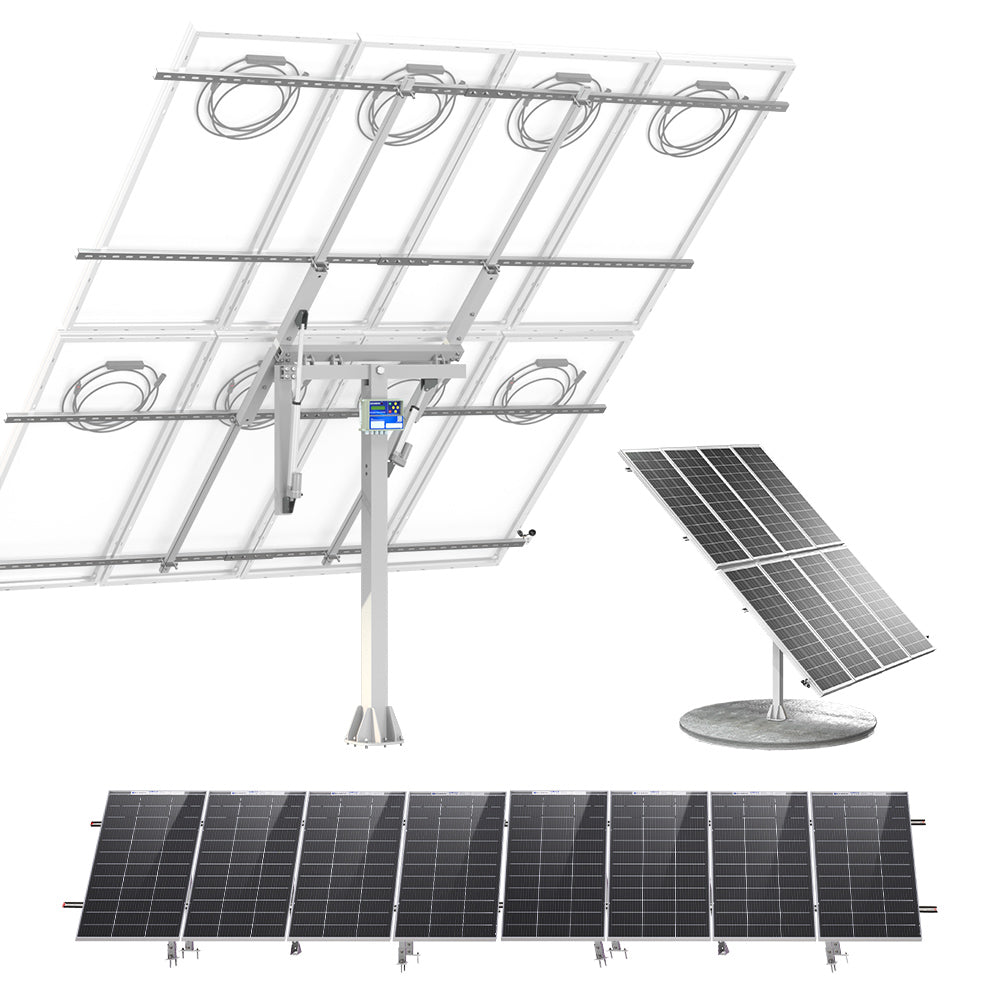
Solar tracking systems are integral to maximizing solar energy efficiency and are categorized based on their movement patterns. These systems are designed with axes that facilitate movement: two horizontal axes and one vertical axis.
The solar panels or reflective surfaces can achieve the optimal angle for maximum sunlight absorption by rotating around these axes. There are two primary types of solar tracking systems: single-axis and dual-axis. Single-axis trackers rotate around one axis, typically aligning east to west, while dual-axis trackers manoeuvre around both axes simultaneously, offering a more comprehensive range of motion.
Application of Single-Axis Tracking System
Single-axis trackers are known for their simplicity and efficiency. They typically move from east to west, following the sun's path across the sky. This type of system utilizes a single angle as its axis of rotation, which can enhance electricity production by over 30%. Single-axis trackers are efficient and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for improving the performance of solar installations.
These trackers are particularly effective during the summer and spring when the sun is higher in the sky. However, their efficiency diminishes as they are installed further north, where the solar angle varies more significantly between summer and winter.
During other times of the year, especially at higher latitudes, the performance of single-axis trackers decreases due to the sun's horizontal position. In such scenarios, vertical axis trackers are more advantageous, as they can adjust to the sun's position throughout the year, including winter.
Horizontal Single-Axis Solar Tracker (HSAT)
The Horizontal Single-Axis Solar Tracker (HSAT) is a common type of solar tracker that rotates on a fixed axis parallel to the ground. This east-to-west movement aligns with the sun's path, enhancing solar energy capture. HSATs are cost-effective due to their simple design and reduced need for structural materials. They are particularly effective in regions near the equator, where the sun's path remains consistent throughout the year.
Horizontal Tilted Single-Axis Solar Tracker (HTSAT)
Similar to HSATs, Horizontal Tilted Single-Axis Solar Trackers (HTSATs) also move from east to west. However, they are installed at a fixed tilt, optimizing sun exposure in specific latitudes. While HTSATs are more complex and may require concrete foundations, they are effective in regions where the sun's angle varies significantly with seasons.
Vertical Single-Axis Solar Tracker (VSAT)
Vertical Single-Axis Solar Trackers (VSATs) stand out with their vertical axis of rotation. They are ideal for high-latitude locations where the sun is lower in the sky.
VSATs can maintain a consistent angle with the sun throughout the day, optimizing energy capture in these specific geographic conditions. However, they require more space to avoid shading and have a lower power density per acre.
Vertical-Tilted Single-Axis Solar Tracker (VTSAT)
Vertical-Tilted Single-Axis Solar Trackers (VTSATs) combine features of vertical and tilted trackers. They rotate on a vertical axis and are tilted horizontally. This allows for improved energy harvest compared to horizontal trackers, especially in locations with significant sun elevation variations. VTSATs, however, demand more robust structural support due to increased wind loading.
Advantages of Single-Axis Solar Tracking System
Single-axis solar trackers offer a blend of efficiency and practicality, making them popular in the solar energy sector. Here are the key advantages of single-axis solar tracking systems, outlined for a clear understanding of their impact and value:
- Reliability: Single-axis trackers are known for their high reliability.
- Longer lifespan: They typically have a longer lifespan compared to dual-axis trackers.
- Cost-effectiveness: These trackers are less expensive than dual-axis trackers due to their simpler mechanism and lower operational costs.
- Efficiency: Single-axis trackers are about 32.17% more efficient than fixed solar tracker mount panels.
- Consistent power output: They track the sun from east to west, ensuring consistent power output throughout the day.
- Increased annual power: Single-axis trackers can generate 15-16% more yearly power than static solar installations of the same capacity.
- Optimal space utilization: These systems offer the highest density of photovoltaic (PV) panel placement per square area.
- Faster return on investment: The investment payback period for solar projects using single-axis trackers is generally shorter, leading to increased profits.
- Maintenance: While they require some maintenance, the overall benefits outweigh the upkeep efforts.
These advantages highlight why single-axis solar trackers are efficient and economical for enhancing solar energy production.
Disadvantages of Single-Axis Solar Tracking System
While single-axis solar trackers offer numerous benefits, it's essential also to consider their limitations. Understanding these disadvantages is crucial for making informed decisions in solar energy projects. Here are the key drawbacks:
- Lower output in sunny conditions: Single-axis trackers have a lower energy output in consistently sunny conditions than dual-axis trackers.
- Limited technological upgrade: The scope for technological advancements in single-axis trackers could be more extensive.
- Geographical limitations: Their effectiveness decreases in higher latitudes due to significant variance in the solar angle between seasons.
- Maintenance requirements: Regular maintenance is needed to ensure optimal functioning, which can add to the long-term costs.
- Less flexibility in tracking: Single-axis trackers do not track the sun as comprehensively as dual-axis systems, potentially missing out on optimal sun exposure at certain times of the day or year.
The Future Scope of Solar Tracking Systems
The solar tracking system market, including single- and dual-axis trackers, is poised for significant growth. Essential for maximizing solar power efficiency, these systems are increasingly important in diverse environments and solar panel types. Solar installers must consider budget, terrain, climate, and system lifespan to choose the right tracker.
The industry's growth prospects are strong. Valued at $2.92 billion in 2018, the global solar tracker market is expected to grow at a 14.1% CAGR through 2025, driven by rising demand for photovoltaic cells. This trend indicates a bright future for solar trackers in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of solar energy systems worldwide.
Final Thoughts
Solar trackers are vital to enhancing solar panel efficiency and are suitable for various environments. The choice between single-axis and dual-axis trackers depends on specific project requirements.
With the solar tracker market poised for growth, these technologies are essential in the global transition to renewable energy. The future of solar energy, bolstered by advanced tracking systems, is promising and vital.